Family arguments are a way of life. We live, we love, we argue, we make up. Research has made it clear that the way we argue carries more heft in determining relationship quality than whether or not we argue, or how much. Fighting filthy will bring us undone. Fighting fair, on the other hand will keep relationships intact.
People and families have a characteristic way of fighting and each is fed by a different part of the brain. New research is challenging people to look at how their brain influences how they fight, with a view to learning more adaptive ways to engage in conflict and avoid the scalding heat of battle.
The Scottish Centre for Conflict Resolution has developed a test for this very purpose. The ‘Monkey v Lizard’ quiz was designed to give people a better idea of what part of their brain they are using when they argue. With this information, people are then well positioned to make deliberate choices around how they ‘do’ conflict.
Monkey v Lizard. Now to explain …
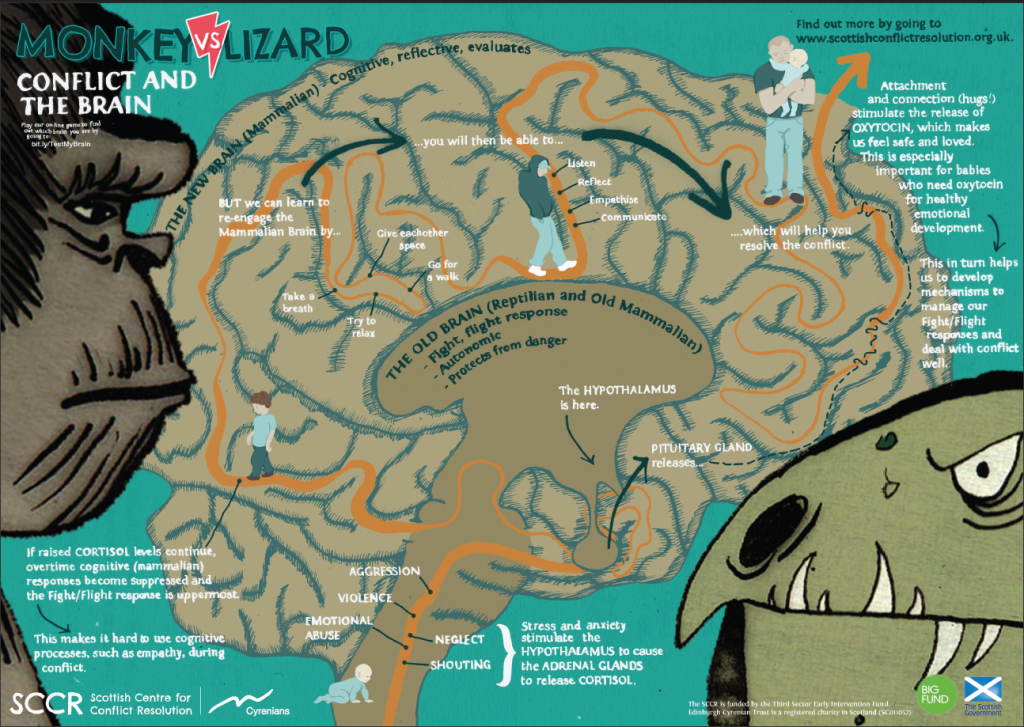
There are two parts of our brain that are called into play when we argue. The Old Brain (the lizard) is the primal ‘fight or flight’ response. All action and not a lot of thought. The other is called the New Brain (the monkey) and involves cognitive (thought) processes such as empathy, reflection and understanding.
The Old Brain is driven to protect us from threat by physically preparing us to fight for our life or run for it. It can come in handy when there’s, say, a bus hurtling towards us and we need to get out of the way. It’s not so handy when the issue is that of Oreos, or more specifically, that someone has taken the last one.
When there’s no need for a physical response (no need to fight, no need to flee), the cortisol builds up. As this happens, the thinking part of the New Brain that empathises, reflects and understands, gets sidelined in favour of the more primitive, automatic, unthinking part. When this happens, there will likely be yelling, personal sledging and aggression. Nobody listens and nobody is heard. Disrespect will be a hallmark.
The New Brain (the monkey), on the other hand is the thinker. When this part of the brain is at the helm, we’re likely to slow things down before we respond, check things out, reason, listen, reflect, empathise and communicate. When the New Brain drives behaviour, people feel heard, validated and understood. This doesn’t mean everyone agrees – not at all. What it means is that people and points of view are respected and relationships remain intact. There’s less ‘agro’ and more respect.
And now what to do about it.
The first step to bringing harmony to the home is being aware of what you’re doing that could do with some tweaking. Just because you’ve always done things a certain way, doesn’t mean you have keep doing them that way. By being aware of what you’re doing, behaviour becomes less automatic and you start to realise you have choices about how to respond. It’s always good to learn that you can do something better – it means you’re human – and a pretty good one if you’re open to change.
Ready to give it a go?
You’ll find the Monkey v Lizard Quiz here. It’s quick – like, 10 questions quick – and you’ll be learning something about yourself in the process. What’s not to love about that?
If your house is getting a bit hot headed, the Scottish Centre for Conflict Resolution has a website with free resources and practical tips. You’ll find their excellent resources here. There’s advice for parents and carers and separate advice for young people. They also tailor advice according to the issue.
An easy way to calm the lizard.
If a battle feels looming, one of the ways to engage the new, thinking part of the brain and calm the old, primal part of the brain is by deep, slow breathing. This has been found to lower cortisol levels and reverse the fight or flight response. It’s why taking short space from each other before things overheat is important. It lets the Old Brain (the lizard) disengage and the New Brain (the monkey) come into play.
And finally …
Conflict is a way of life. In a house with flourishing, independent, curious minds it’s going to happen.
When kids are involved, it’s good to think that we’ve brought them up to think for themselves and to know their own mind. When you raise independent minds who are curious, strong, independent and questioning, there are going to be times when those minds differ from ours. Though it’s hard to be grateful for that when their acquiescence would make things so much easier, the truth is, it’s something to be proud of. What that depends on, of course, is that way the conflict plays out.
When people are not heard, acknowledged and validated, relationships fall apart. If this is something you’re struggling with in your family, take the test with your tribe to first show them that there is a different way of being. Then, have a look at the resources in the link. All change starts with awareness. Being open to change and the impact you have on people, when you’re fighting or otherwise, is the essence of healthy relating and the key to healthy, full relationships.



Very interesting read made a lot if sence as well